23
2025
-
09
Analyzing the brake master cylinder: the soul engine of the automotive braking system.
The brake master cylinder is a core component of the automobile braking system, and its operating mechanism is closely related to driving safety. Understanding the working principle of the brake master cylinder greatly benefits the assessment of daily vehicle conditions and the timely troubleshooting of faults. Now, we will conduct an in-depth analysis of the principles of the brake master cylinder.Basic StructureThe brake master cylinder consists of a pump body, piston, spring, and oil port. The pump body serves as a container for holding other components, ensuring stable operation without external interference. The piston slides within the pump body and is well-sealed, responsible for transmitting pressure. The spring provides the necessary elasticity for the piston to return. The oil port is connected to the brake line, ensuring smooth flow of brake fluid.Preparation for Operation
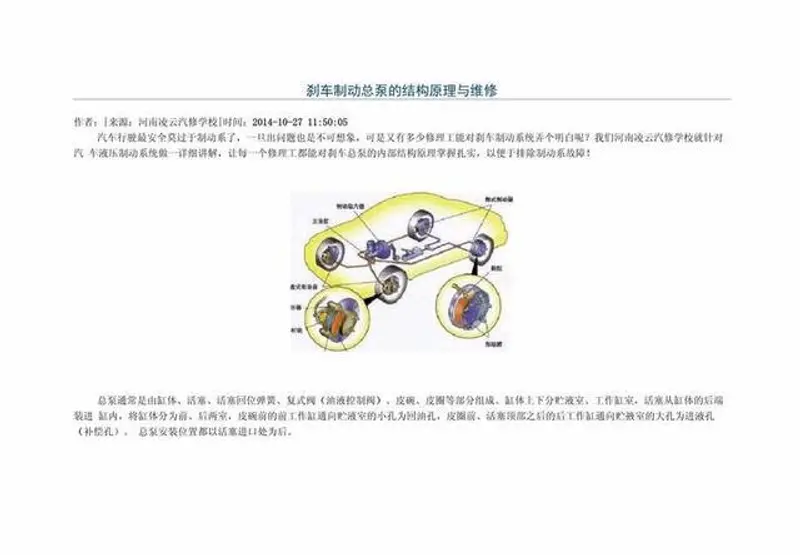
Before starting the vehicle, the piston of the master cylinder is held in place by a spring on one side of the pump body. Brake fluid has flowed into the master cylinder through the inlet, ensuring that the brake system has sufficient fluid medium. At this stage, the various components of the master cylinder are not yet in motion, but they are ready to respond to brake commands at any time.Braking ProcessWhen the brake pedal is pressed, force is transmitted through the push rod to the piston, causing it to move forward within the pump body. At this time, the brake fluid in front of the piston is pressurized, and the pressure begins to rise. Subsequently, high-pressure brake fluid flows from the outlet into each brake caliper, driving the caliper pistons. Finally, the brake pads create friction against the brake disc or drum, achieving the effect of stopping the vehicle.Reset Stage
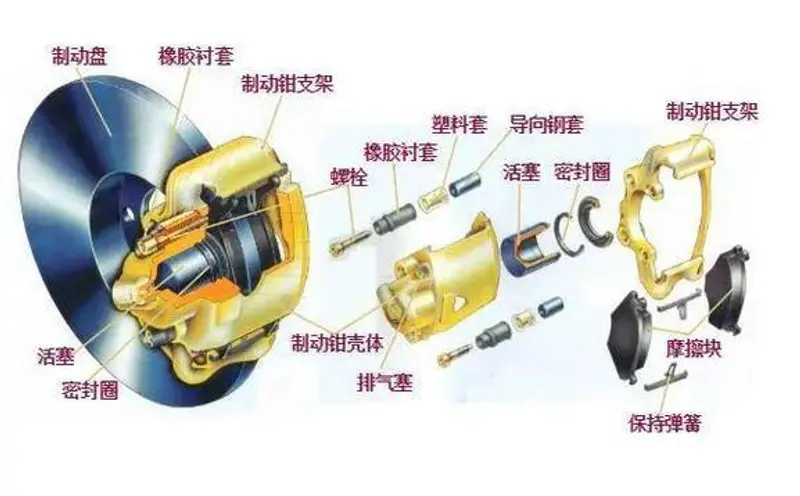
Once the brake pedal is released, the external force acting on the master cylinder piston disappears. Then, the spring's elasticity quickly returns the piston to its starting point. At the same time, the brake fluid in the brake caliper, under the influence of the pressure difference, flows back to the master cylinder through the oil pipe, preparing for the next braking operation.Common influences.
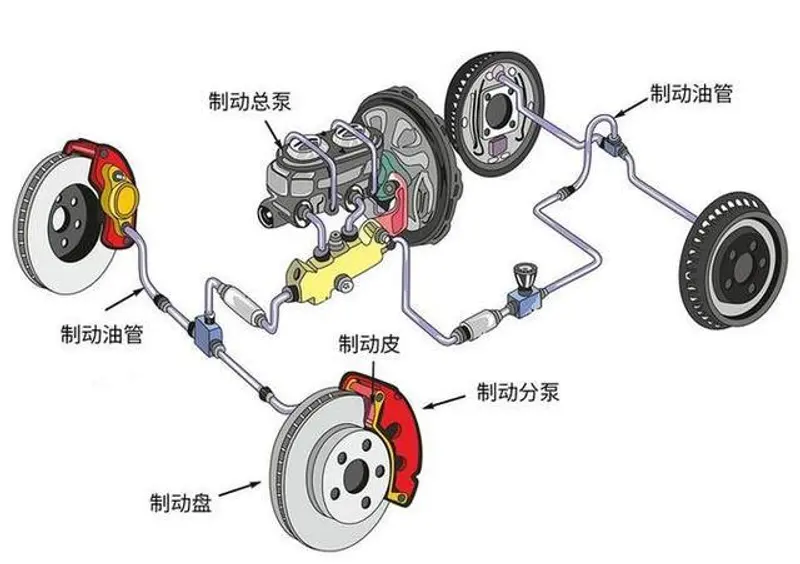
The operation of the brake master cylinder is affected by various factors, such as the quality of the brake fluid. If its boiling point is too low or its corrosion resistance is insufficient, cavitation can easily occur, which in turn affects braking effectiveness. Piston wear and poor sealing may also lead to brake fluid leaks and pressure drops, thus jeopardizing braking safety. Therefore, in daily use, we need to closely monitor the condition of the braking system.
Previous Page
Previous Page



