19
2025
-
07
Truck Encyclopedia (11): In addition to the auxiliary braking of the liquid slow
At present, there are many common truck auxiliary braking technologies, which can be roughly divided into three categories: in-cylinder brakes, exhaust brakes and hydraulic retarders.
▎ It is strictly forbidden to coast in neutral gear - the vehicle assists braking
Why is it strictly forbidden to coast in neutral, because coasting in neutral will run faster and faster.
As we all know, engine work consists of a complex set of mechanical structures, which usually exist as a power output.
On the downhill section, when the driver releases the accelerator pedal, the engine stops injecting, and the drive wheel and transmission system drive the engine crankshaft in reverse, and the engine switches to provide deceleration braking. Through the driver's reasonable gear selection, the engine can play a better braking effect.
However, our trucks usually carry tens of tons of cargo, and the steep slopes are steep, so the braking ability of the engine itself is not enough. So people came up with ways to provide greater braking effects for the engine - exhaust braking and in-cylinder braking.
● Low-cost auxiliary braking - exhaust brake
Before we begin, let's review the working principle of the engine. The engine work is composed of four steps: air intake, compression, combustion expansion, and exhaust.
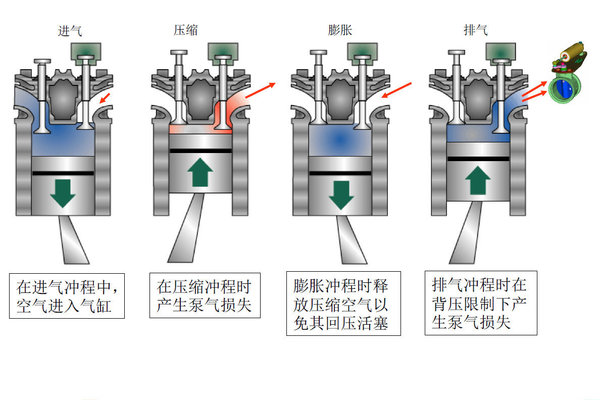
Exhaust braking is the principle of using the cycle of the engine to do work, in the exhaust link, through a valve to close the exhaust port, so that the piston is under pressure from the exhaust pipe when exhausting, hindering the piston stroke and reducing the engine speed.
To put it simply, exhaust brake is to install an exhaust suppression device in the engine exhaust system, which can control the exhaust volume of the engine through the switch of the butterfly valve and prevent the piston from rising, so as to achieve the purpose of controlling the vehicle speed.
However, the effect of reducing the engine speed is not obvious only by closing the exhaust pipe to increase the exhaust back pressure, which is only about 20%-30% of the engine power.
Merit:
The price is cheap.
Shortcoming:
Low braking efficiency.
● Mainstream high efficiency - in-cylinder braking
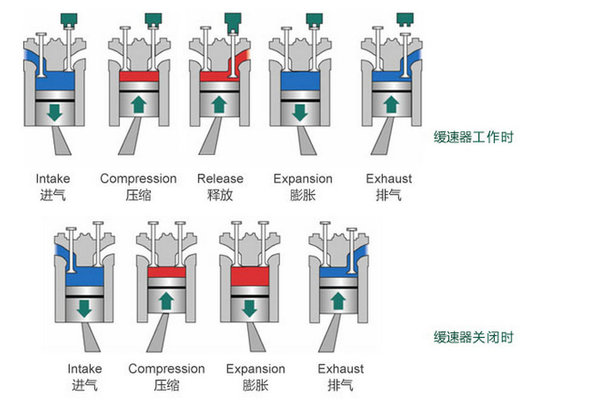
At present, the mainstream in-cylinder braking technology is divided into compression-release braking and deflection braking. Let's start with compression-release brakes.
The compression-release brake also uses the principle of engine work, but at the end of the compression link, the exhaust valve is opened to discharge the compressed high-pressure air, and the piston loses the power to do work downward.
Then, at the stage where the combustion expansion (work) should be done, the exhaust valve closes quickly, and there is only normal atmospheric pressure in the cylinder, and the piston descends to form a vacuum. In this way, one plus one minus two links, the braking effect of the engine is greatly improved.
Simply put, compression-release brakes change the engine output to negative output by controlling the exhaust valve opening and closing time, so that the engine brings greater braking capacity.
Regarding compression release braking, you can also read this article "Introduction to the Engine Braking Principle of Engine Second Air Compressor".
The compression release brake technology is relatively mature, and the price is also more advantageous, about 5,000 yuan. Since it is valve controlled, the control mechanism is integrated inside the engine and does not take up additional space. The braking efficiency is also high, reaching 80%-90% of the engine's output.
Merit:
Affordable, does not take up extra space, requires no maintenance, and has high braking efficiency.
Shortcoming:
There are no obvious shortcomings, and the braking efficiency is slightly worse than that of the hydraulic retarder.
There are two types of deflated braking: active deflating and passive deflation. It can be roughly considered a simplified version of compression-release brakes. The degassing brake is also in the compression link, so that the exhaust valve is opened to discharge the high-pressure gas in the cylinder, so that the piston loses the ability to move downward, so as to reduce the engine speed.
Passive deflation braking needs to work in tandem with the exhaust brake, and when the exhaust brake is on, the increased exhaust back pressure pushes the exhaust door open for deflation.
The active degassing brake achieves the effect of degassing braking by controlling the opening of the exhaust valve through the solenoid valve during the entire compression stroke.
The price of the deflated brake is cheaper than the compression type, and the braking efficiency is about 40% higher than that of the exhaust brake. But it still can't meet the braking needs of truck long-term downhill.
Merit:
It is inexpensive, does not take up extra space, and requires no maintenance.
Shortcoming:
The braking efficiency is low and cannot meet the braking needs of the truck's long downhill.
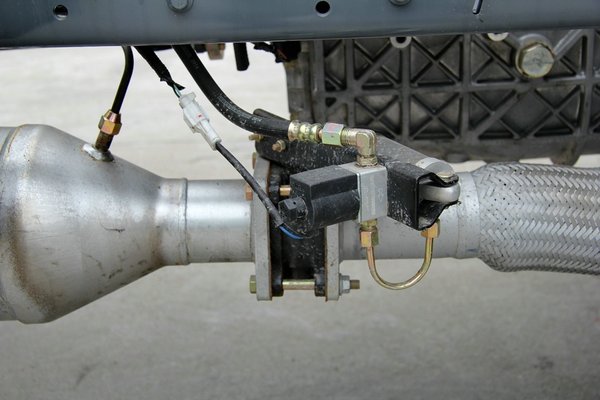
● Good, but expensive – hydraulic retarder
The hydraulic retarder works similarly to the hydraulic torsion converter of an AT transmission. The torque converter is equipped with two turbine blades in a space filled with oil, which are connected to the power output and input terminals respectively, and the power conversion between the two blades is realized by liquid damping.
Unlike the AT transmission, one blade of the hydraulic retarder is the stator, that is, the blade that does not rotate, and the other blade follows the output shaft.
Under normal circumstances, the oil in the working chamber is emptied to avoid consuming engine power.
When deceleration is required, the oil enters the working cavity under the action of compressed air, and the rotor drives the oil to rotate, and the action of the oil is transmitted to the stator to produce a reaction, hindering the rotation of the rotor and realizing the deceleration effect.
The braking efficiency of the hydraulic retarder is high, taking a certain brand of hydraulic retarder as an example, its braking power can reach 645kW and the maximum braking torque is 3000 Nm.
The cost of hydraulic retarder installation and optional is about 2-30,000 yuan. However, when the hydraulic retarder is installed in the later stage, it is limited by the frame size and engine heat dissipation power, and some early models and models with less engine horsepower are not suitable for installation.
Merit:
High braking efficiency and simple maintenance.
Shortcoming:
The price is more expensive, occupies a small part of the chassis space, and has certain requirements for the engine cooling system.
● Eddy current retarder
Eddy current retarder is commonly known as electric brake. Generally, it is composed of stator, rotor and fixed bracket, etc., and realizes the purpose of braking through electromagnetic principle.
When the eddy current retarder works, the rotor rotates with the drive shaft, and the stator coil is energized to generate a magnetic field. The rotor cuts the magnetic field lines generated by the stator so that the stator exerts an electromagnetic force on the rotor that prevents the rotor from rotating, resulting in a braking torque.
At the same time, eddy currents circulate inside the rotor disc with a certain resistance, and the thermal effect of the resistance will convert the electrical energy into heat energy, so that the kinetic energy of the vehicle will be converted into heat energy through electromagnetic induction and resistance heating.
Due to the working principle, the eddy current retarder has a fast reaction speed and timely braking response. However, the heat dissipation is mainly through air cooling, and the working temperature is higher when the vehicle speed is relatively low and when braking continuously, generally reaching more than 600 °C. The installation cost is about 10,000 yuan, and it is rarely assembled on trucks and is mostly used for buses.
Merit:
The braking response is fast and the price is cheaper than that of hydraulic retarders.
Shortcoming:
Large size, high heat dissipation requirements, high operating temperature.
After reading the in-cylinder brake, exhaust brake and hydraulic retarder, I believe everyone has a certain understanding of these auxiliary brakes. The outstanding performance and easy maintenance of the hydraulic retarder have become the biggest winners of this auxiliary braking, but if you want to enjoy this "artifact", you naturally need to pay some cost.