20
2025
-
06
Basic knowledge of automobiles (2) The structure of automobile chassis
Hello everyone, the basics of cars are back again. In the last issue, we started from the most basic and divided the car into four major parts (friends who don't know which four parts can click here to review: "Automobile Basic Knowledge (1) The Overall Structure of the Car"). So what about the content of this issue, let's talk about one of the contents: chassis.
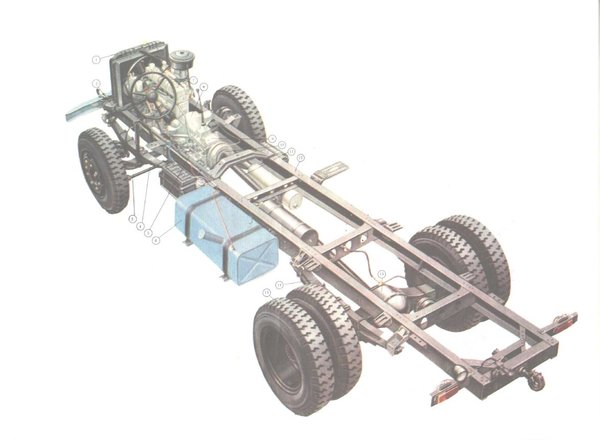
When it comes to the chassis of the car, what comes to mind is the parts and assemblies that are densely distributed throughout the frame. Of course, old drivers are very familiar with these things, but new cardholders will inevitably feel clueless. Therefore, we first need to classify the chassis according to function.
Generally speaking, the chassis can be divided into four major systems:
1) Driving system
2) Drive train
3) Brake system
4) Steering system
Let's explain the old rules one by one.
● Driving system
For a car, the first function to be done is - active. In order to meet this function, a car must have at least one shelf, a few wheels - these things, which make up the driving system of the vehicle.
Of course, "active" is only the most basic requirement for the driving system. For a normal driving vehicle, the driving system needs to ensure that the vehicle is stable, withstand and mitigate the impact of the road surface, and ensure that the vehicle can drive normally. To put it simply, it is to make the vehicle able to walk steadily and comfortably.
Therefore, the words we usually talk about "vehicle driving stability" and "handling" are actually used to evaluate the level of the car's driving system.
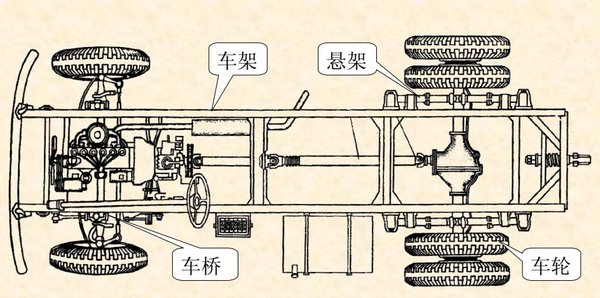
According to different vehicle needs, there are different types of driving systems: wheeled, half-tracked, full-tracked, wheel-tracked and so on. Obviously, the common cars on our roads are wheeled car driving systems, which are composed of four parts: frame, suspension, axles, and wheels. The four parts are connected together in turn to ensure the vehicle's driving ability.
● Drive train
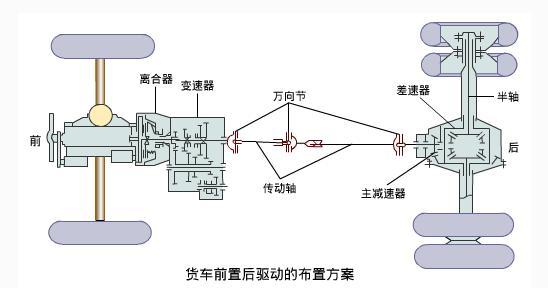
After the driving system has set up the frame of the vehicle, we need to think about how to make the vehicle move. The engine provides power to the vehicle, but because it revs too high, it is obviously not suitable to be connected directly to the wheels, so the drivetrain is needed to transfer the power.
The drive train is generally composed of: clutch, gearbox, universal transmission, final reducer, differential, and drive half shaft. The power generated by the engine is sequentially transferred to the wheels through these components.
Depending on the location of the engine and transaxle, the drive train can be divided into the following forms:
Front-wheel drive (FF), front-rear wheel drive (FR), rear-wheel drive (RR), mid-rear-wheel drive (MR), four-wheel drive (4WD), and more. The selection of different drive forms should mainly take into account the distribution of the front and rear weight of the vehicle, the size of the space, and the application scenario.
For example, ordinary family cars adopt front-wheel drive, which can make the structure more compact, save space for passengers, and the front engine can also improve the cooling effect and increase the safety of the vehicle; The counterweight of the truck is further back, so the choice of rear drive can increase the adhesion of the wheels, while the front engine can leave more loading space for the rear; The bus also chooses rear-wheel drive for better adhesion, and if the engine is front-loaded, then a propeller shaft is needed to transmit power, which will occupy cabin space and reduce transmission efficiency. Therefore, buses mostly use rear-mounted rear-wheel drive.
● Brake system
If you have a drivetrain, you definitely need a brake system – to be able to move, but also to be able to stop.
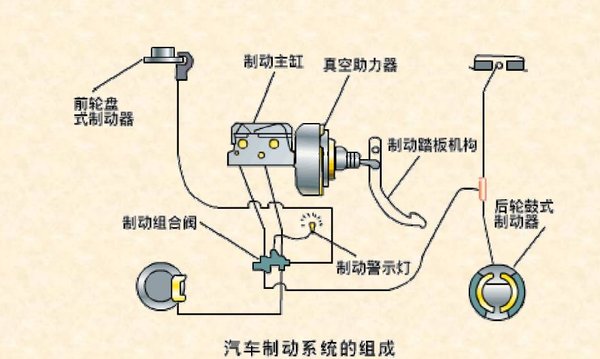
The braking system is composed of four parts: energy supply device (brake oil or air pump, air storage tank, etc.), control device (brake pedal, various brake valves, etc.), transmission device (such as brake cylinder, etc.) and brake.
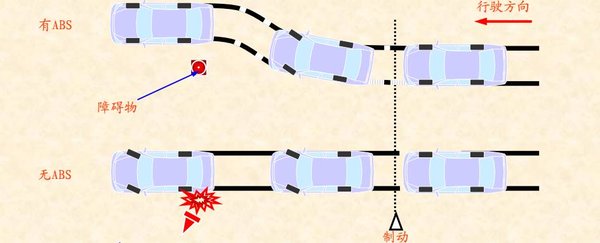
The well-known ABS and EBS systems are involved in the "control device" of the braking system. The traditional brake control is completely judged by the person and the brake pedal is pressed; The ABS system is judged by the computer and directly controls the brakes through the transmission.
Many people know that an important indicator to evaluate the braking performance of a vehicle is the braking distance. But that's just one of them. In addition to the braking distance, it is also necessary to take into account the constancy of the brakes (resistance to thermal and water decay) and the directional stability of the vehicle during braking (deviation, side slip, loss of steerability, etc.).
For example, disc brakes are excellent in terms of constancy, but they don't have as much stopping power as drum brakes; Electronic assistance systems, such as ABS, improve the vehicle's directional stability when braking.
● Steering system
With the first three systems, the vehicle can walk and stop, but in order to get on the road, one condition must be met: it can control the direction. That's why you need the steering system of the vehicle.
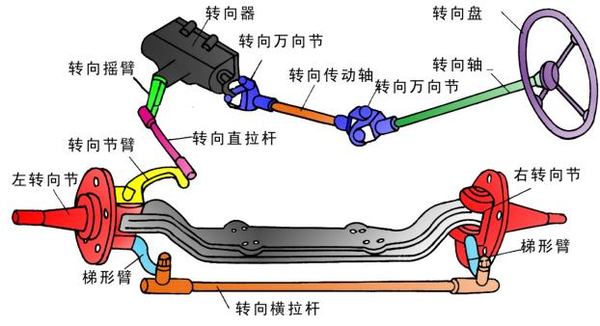
转向系主要由:转向操控机构、转向器、转向传动机构三部分组成。
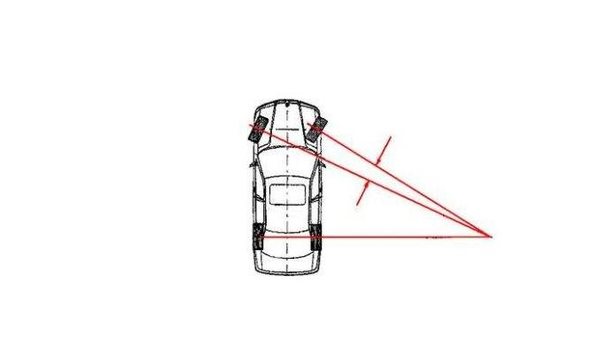
Theoretically, when a car is turning, all wheels should circle around the same center to avoid tire wear. That is, the corners of the two wheels should be different, and the corners of the inside wheels should be larger than the outside wheels, and a certain functional relationship should be satisfied.
But in fact, all kinds of existing steering mechanisms can not fully guarantee this relationship, so the problem of wheel slippage cannot be completely eliminated technically. Especially for trucks with dual drive axles, it is inevitable to eat tires. But on the other hand, different manufacturers have different investments in this area, and the degree of tire eating will be correspondingly different.
● Summary
Okay, that's all for today. After we divide the chassis into these four categories, when the vehicle encounters a problem, we can clearly determine which system is wrong, and then troubleshoot the problem from this system, so that it will be more clueless.
Previous Page
Previous Page